In the Anaheim City School District, where most students are low-income and struggling to learn English, teachers need special training, extra tutoring time and lots of visual materials to help their pupils achieve at grade level.
In the well-heeled Palos Verdes Peninsula Unified School District, poverty and limited English are not widespread problems. But officials there say their student needs include more expensive Advanced Placement classes to challenge them with college-level material in high school.
Who should get more state educational dollars? Last week, school districts got their first glimpse of how that question would be answered under Gov. Jerry Brown's proposed new funding formula: Anaheim would receive an estimated $11,656 per student annually; Palos Verdes would get $8,429 by the time the plan is fully implemented in seven years.
And that disparity draws distinctly different reactions.
"It's great news," said Darren Dang, Anaheim's assistant superintendent of administrative services. "Given our demographics, we'll be getting much-needed resources for our students."
But Lydia Cano, Palos Verdes' deputy superintendent of business services, said she believed the new scheme would shortchange her students. Disadvantaged students already receive a bigger share of state and federal dollars, she said.
"It's not fair," she said. "It will make the divide even bigger."
In the most significant change in four decades in how school dollars would be distributed, Brown is proposing to give all districts a base grant, then add an extra 35% of that for each student who is low-income, struggling with English or in foster care. If such students make up more than 50% of a district's population, another 35%supplement would be given.
The formula is part of Brown's proposed budget, which requires the Legislature's approval.
Under the proposal, the state would do away with most so-called categorical funding — which was earmarked for such specific uses as textbooks, remediation and low-income student aid. Instead, the money would be given directly to districts with no strings attached, to promote Brown's goal of greater local control.
The plan is aimed at reforming what most educators agree is an inequitable, burdensome and overly complex funding system. It is grounded in a 2008 report coauthored by state Board of Education President Michael Kirst that compiled research showing that parental income and English language ability are two critical factors in academic achievement.
Kirst argued that it was more important to help needy students gain grade-level skills than it is to provide college-level work for top-achieving high schoolers. "These are judgments about political priorities," he said.
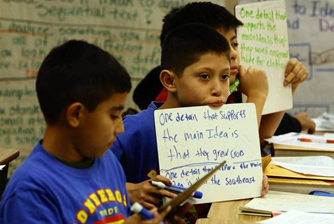
About 20 states currently distribute extra dollars to needier students, including Rhode Island and New York, according to Margaret Weston of the Public Policy Institute of California. Poor districts in California already receive about 20% more in state and federal dollars than do affluent ones, but Brown's formula would increase that share, she said.
After four years of crippling budget cuts, the Los Angeles Unified School District is expected to receive an estimated boost of $820 more per student over the next two years under Brown's proposal. By 2020, funding is expected to grow to $11,993 per student from $7,509 last year.
L.A. Supt. John Deasy hailed the governor's proposal. "It's morally the right thing to do and educationally the sound thing to do," he said.
Like many administrators, however, Deasy cautioned that it would take a few years of increases to make up for the state's devastating reductions since 2007. New spending could possibly begin in 2015, he said, adding that he would recommend restorations in summer school, counselors, arts and support staff, among other things.
He also said he would make it the district's "policy and practice" to send the state dollars for disadvantaged students directly to their schools to help them. Some officials, such as Dang in Anaheim, have expressed concerns about possible pressure to use the money for salary hikes.
Over the next five years, per-student funding is expected to grow by about $2,700, the state estimates showed. All school districts and charter schools would receive at least as much money this year as last.
In Los Angeles County, funding estimates range from a low of $7,863 per student in the Hermosa Beach City School District to $13,569 for Animo Leadership High, an independent charter school in Inglewood.
Long Beach, San Bernardino City and Santa Ana unified all are estimated to receive funding boosts of $800 to $1,000 per student over the next two years. But the state projects an increase of less than half that for more affluent districts, such as San Marino, Palos Verdes Peninsula and Manhattan Beach unified.
Julie Boucher, San Marino's assistant superintendent of business services, said she was dismayed that Brown was not proposing to first restore general funding that the state has cut since 2007 before allocating additional dollars to specific students.
San Marino's state funding has been slashed by $17 million since 2008 — a total equivalent to 60% of its annual budget. The district has received $3.1 million annually from its nonprofit fundraising foundation and $5.1 million from a parcel tax but still has worked with its employee unions to freeze salaries, require larger contributions for healthcare, cut 26 teaching positions and shorten the school calendar with unpaid furlough days, she said.
"It does not seem equitable given the fact that we're all down," she said of Brown's proposal. "First we need to be made whole. Don't rob Peter to pay Paul."
During a recent visit to Ponderosa Elementary School in Anaheim, however, educators demonstrated how teaching lower-income English learners is more costly and time-consuming.
In Bernadette Grzechowiak's fifth-grade classroom, for instance, students were learning how to find main ideas in a passage about Native Americans. But unlike fluent English speakers, she said, those with limited language skills need far more visual aids — presented every 60 to 90 seconds, according to research. Her room is filled with graphics about colonial America and sentence frames to teach them academic language, such as "One detail that supports the main idea is…"
Grzechowiak said she learned those and other techniques from a district-paid teaching coach.
Ponderosa has also spent $10,000 on a science book series heavy on photos and graphics to help students learning English. And the school has two full-time teachers to provide extra support for struggling students and a bilingual community liaison to help educate the school's largely immigrant parents about their children's academic needs.
"Kids are so hungry and ready to learn," said Maria Villegas, the principal. "It just takes time, opportunity and having a great staff."
Be the first to comment
Sign in with
Facebook Twitter